How to Choose Hearing Aids for an Active Lifestyle
If you enjoy hiking, playing tennis, working in your garden or
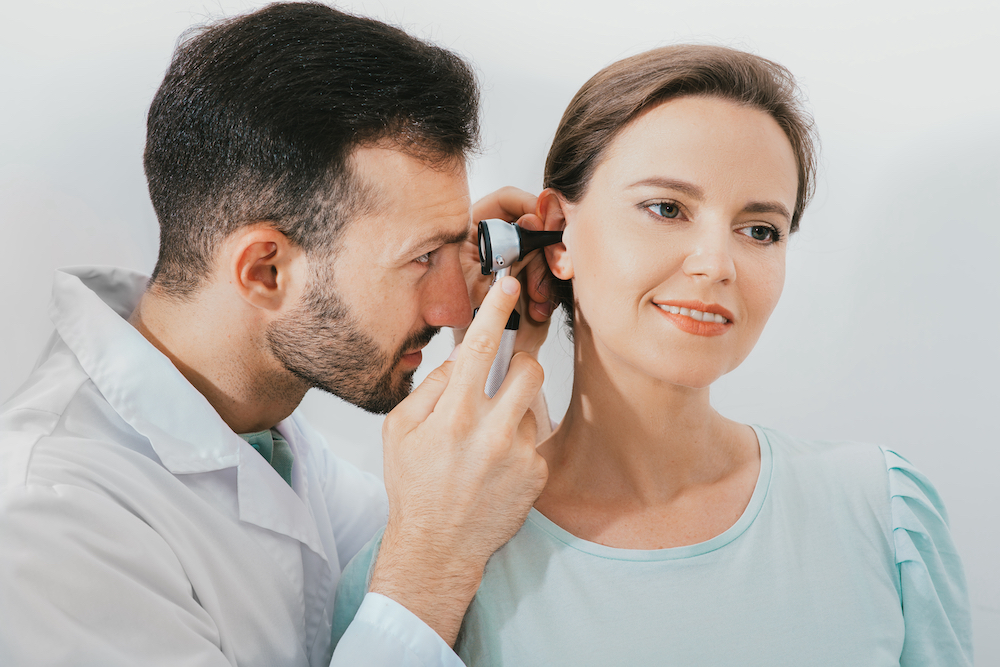
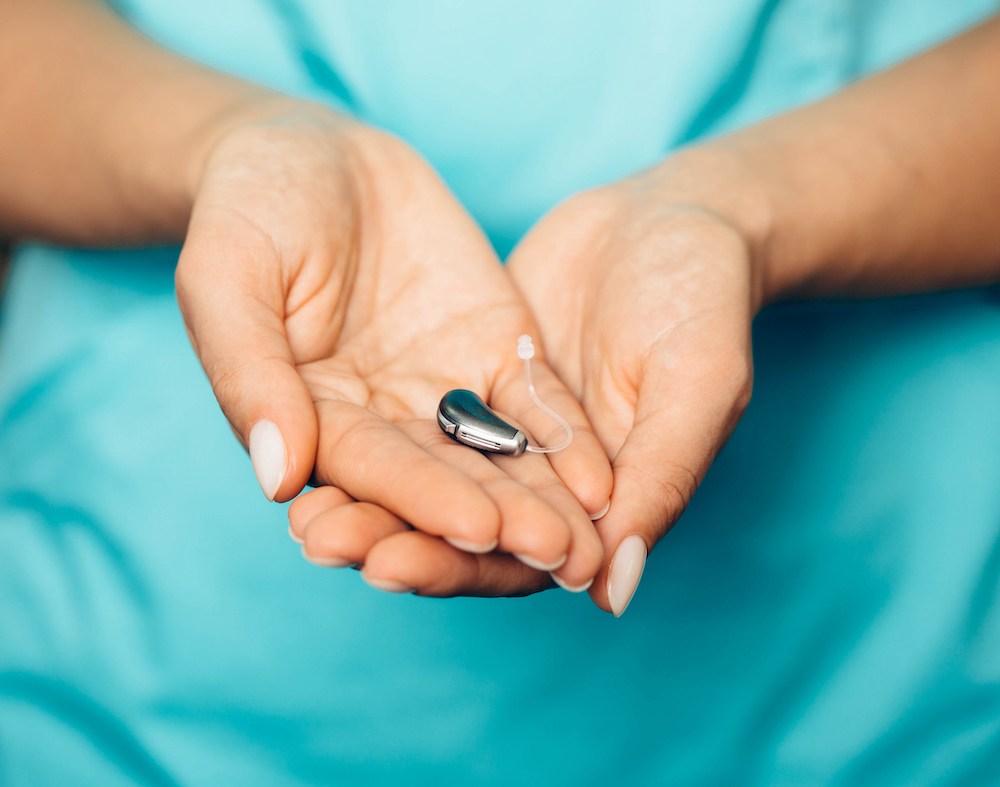


If you enjoy hiking, playing tennis, working in your garden or
Hearing loss can make understanding speech difficult. You may notice that
In the world of hearing care, it’s important to trust the right